Title: Identification of Peptides with Tolerogenic Potential in a Hydrolyzed Whey‐Based Infant Formula
| Authors: | Joost W. Gouw, Juandy Jo, Laura A. P. M. Meulenbroek, T. Sam Heijjer, Erica Kremer, Elena Sandalova, André C. Knulst, Prescilla V. Jeurink, Johan Garssen, Anneke Rijnierse, Léon M. J. Knippels |
| Published: | 2018 |
| Journal: | Clinical and Experimental Allergy |
Food allergy in general and cow’s milk allergy is a widespread health problem and is on the rise. It is estimated that half of the EU population will have an allergy by 2025. By 2050, four billion people will be affected by allergy with an earlier onset and with more severe symptoms. Currently, more than 2% of children living in developed countries are allergic to cow’s milk protein and the symptoms can be severe. Although most children eventually outgrow cow’s milk allergy, they are susceptible to develop other kind of allergies later in life. Allergic children have a lower quality of life as they need to avoid specific food that is causing the allergy. Therefore, our newest approach in the allergy prevention program is aiming to reduce the risk of developing allergy in infants who are at risk. This shall be achieved by combining controlled protein exposure with modulation of the gut microbiota, in our specific hydrolysed protein formula (pHF) with synbiotics.
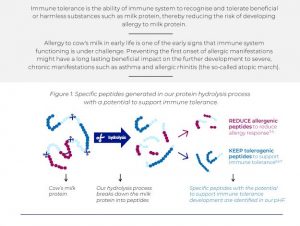
In this newest publication pertaining to the controlled protein exposure, we have used a sophisticated tool, which can be seen as a molecular microscope, to identify very specific protein fragments (peptides) present in our pHF formula. Through in-depth investigation of those specific peptides, we demonstrated that they could be recognized by the human immune system. These functional protein fragments in turn can potentially support the development of oral tolerance to cow’s milk protein. Taken together, we have confirmed the presence of specific protein fragments in the pHF formula, and have shown that those peptides can be recognized by the immune system, thus having a good potential to minimize the risk to suffer from food allergy.
Click here to access the full publication.
Click on the images below to access our publication summary.